

It requires placing a solid silicone band or a silicone sponge under the tear/s and detached retina, draining the fluid from under the retina by cutting through the wall of the eye, thus allowing the retina to settle on the wall of the eye (flattening), and either freezing or lasering around the retinal tear/s to create an adhesion between the retina and the wall of the eye. This procedure requires an admission into either the hospital or a surgical outpatient facility and is performed in an operating room, either under local or general anesthesia. The second method is called a “sclera buckle “. This is often considered a hardship, but the procedure takes a much shorter time, as is the recuperative period, and the patient can usually return to normal activity in approximately 3 weeks.
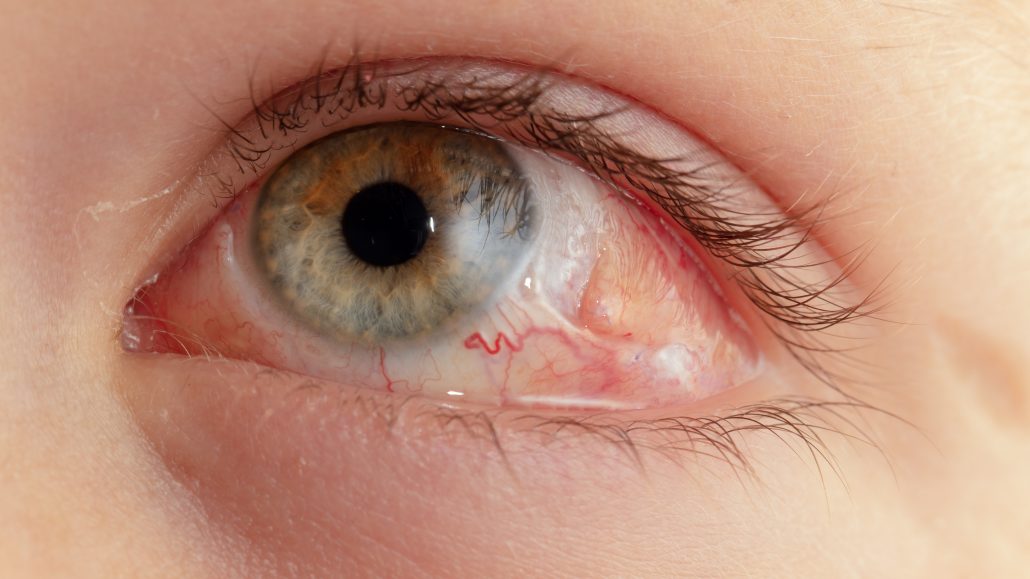
This, in some cases, will require the patient to lie on their side for several days. Retinal detachments treated in this manner are usually associated with few and small retinal tears with a detachment located above a horizontal line across the center of the eye.Īs stated, after the gas bubble is injected into the eye, the patient has to be positioned in such a way as to cover the tear. Once all the fluid under the retina has been removed and the retina around the retinal tear/s is flat, then the second step would be either laser and/or freezing (cryo-therapy) is performed around the tear, creating a low-grade inflammatory reaction which then results in an adherence of the retina to the wall of the eye. This prevents further migration of fluid into the subretinal space, allowing the normal function of the eye to pump out the fluid which has already accumulated under the retina. It generally, involves two steps, the first is the injection of a small long-acting gas bubble into the eye, and positioning the patient is such a manner that the gas bubble covers the retinal tear/s. The first method, which can be performed in the office setting is call a “pneumatic retinopexy “. The one that would be recommended by your retinal surgeon would depend upon the extent of the retinal detachment, the location of the retinal tear/s, the evidence of any scar tissue formation, and the presence of prior cataract surgery. There are three ways of treating a retinal detachment. What Are The Symptoms Of A Retinal Detachment? They most commonly occur in patients with advance diabetic eye disease, after severe ocular trauma, and in patients who have complications after rhegmatogenous retinal detachment surgery. Traction retinal detachments are due to scar tissue formation within the eye. Depending on the location of the tear/s, the separation can occur very gradually, however under the right conditions, it can occur very rapidly. Once a tear occurs, and there is sufficient traction on the edge of the tear, allowing fluid within the eye to migrate under the retina resulting in a retinal detachment. However, in an area where there is a tight attachment of the vitreous to the retina, the constant pulling can result in a tear. With age, the vitreous degenerates and collapses upon itself, thus pulling away from the retina, causing a separation called a (PVD) “posterior vitreous detachment”. This attachment weakens over time, but in some areas may be more firmly attached. Vitreous, in early life, is very clear and attached to the retina. Within the hollow of the eye, there is a gelatinous material called the vitreous.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
